Description
4-Fluoroisobutyr-fentanyl is a synthetic opioid that has garnered attention due to its potent analgesic effects and the risks associated with its misuse. This article delves into the details of 4-Fluoroisobutyrfentanyl, exploring its uses, potential risks, and regulatory landscape.
What is 4-Fluoroisobutyr-fentanyl?
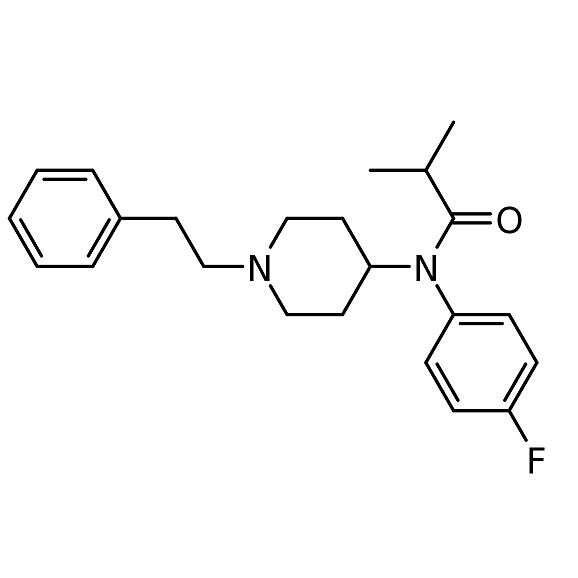
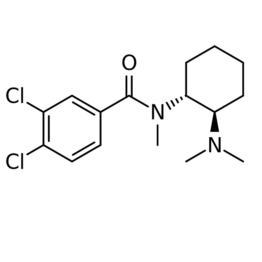
4-Fluoroisobutyr-fentanyl is a chemical compound closely related to fentanyl, a well-known synthetic opioid. It is part of a class of fentanyl analogs designed to mimic the potent pain-relieving effects of fentanyl while differing slightly in chemical structure.
Chemical Structure and Properties
The compound is characterized by the presence of a fluorine atom in its molecular structure, specifically replacing a hydrogen atom in the isobutyrfentanyl molecule. This modification can significantly alter the drug’s pharmacological profile, including its potency, metabolism, and potential for abuse.
Medical and Illicit Uses
While some fentanyl analogs have legitimate medical applications, 4-Fluoroisobutyrfentanyl is primarily encountered in the context of illicit drug use.
Medical Context
In a medical context, fentanyl and its analogs are used for pain management, particularly in patients with severe pain that does not respond to other treatments. These drugs work by binding to opioid receptors in the brain, effectively reducing the perception of pain.
Illicit Use and Abuse
Illicitly, 4-Fluoroisobutyr-fentanyl is often found in counterfeit pharmaceuticals or as an additive to street drugs. Its high potency means that even a small amount can lead to significant effects, which makes it attractive to recreational drug users but also significantly increases the risk of overdose.
Risks and Side Effects
The risks associated with 4-Fluoroisobutyr-fentanyl are substantial, particularly due to its high potency and the potential for misuse.
Overdose and Toxicity
One of the most significant dangers is the risk of overdose. Synthetic opioids like 4-Fluoroisobutyrfentanyl can be many times more potent than heroin or morphine, leading to respiratory depression, coma, and death even at very low doses. The margin for error is extremely narrow, making it easy to unintentionally consume a lethal dose.
Side Effects
Common side effects include drowsiness, dizziness, nausea, constipation, and respiratory depression. Chronic use can lead to tolerance, dependence, and withdrawal symptoms when the drug is not available.
Legal and Regulatory Status
The legal status of 4-Fluoroisobutyrfentanyl varies by country, but many jurisdictions have classified it as a controlled substance due to its potential for abuse and harm.
United States
In the United States, 4-Fluoroisobutyrfentanyl is classified as a Schedule I controlled substance under the Controlled Substances Act. This classification indicates that the drug has a high potential for abuse, no accepted medical use, and a lack of accepted safety for use under medical supervision.
International Regulations
Internationally, the substance is also controlled under various drug scheduling frameworks. Many countries have enacted strict regulations to curb its production, distribution, and use. Regulatory bodies such as the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) monitor and recommend controls on such substances to prevent misuse.
Harm Reduction and Public Health Measures
Given the severe risks associated with 4-Fluoroisobutyrfentanyl, harm reduction strategies are crucial in mitigating its impact on public health.
Education and Awareness
Public health campaigns focused on education and awareness can help inform the public about the dangers of synthetic opioids. These initiatives can reduce the incidence of accidental overdoses by making people aware of the potency and risks of substances like 4-Fluoroisobutyrfentanyl
Access to Treatment
Increasing access to addiction treatment services, including medications like methadone and buprenorphine, can help individuals struggling with opioid dependence. Naloxone, an opioid antagonist, is also essential for reversing overdoses and should be widely available.
Strong policies and effective law enforcement can help reduce the availability of illicit synthetic opioids. International cooperation and comprehensive strategies are required to tackle the global nature of the synthetic opioid crisis.
Conclusion
4-Fluoroisobutyrfentanyl is a potent synthetic opioid with significant risks associated with its use. Understanding its properties, risks, and the regulatory environment is crucial for addressing the challenges it poses. Through a combination of education, harm reduction, and robust legal frameworks, the dangers of 4-Fluoroisobutyrfentanyl can be mitigated, protecting public health and safety.
Mary Miller –
Always helpful, excellent at keeping me informed about supply delays, and very friendly!