Description
In the expansive landscape of novel psychoactive substances, deschloroketamine hydrochloride (DCK) emerges as a compound of increasing interest and intrigue. As a derivative of ketamine, DCK offers unique pharmacological properties that have captured the attention of researchers and enthusiasts alike. Join us on an exploratory journey into the world of DCK, uncovering its origins, effects, potential applications, and associated considerations.
Understanding Deschloroketamine Hydrochloride (2′-Oxo-PCM HCl or DXE, DCK)
Deschloroketamine hydrochloride, also known as 2′-Oxo-PCM HCl or DXE, DCK is a structural analog of ketamine, a dissociative anesthetic and hallucinogenic substance. Chemically, it is characterized by the absence of a chlorine atom at the 2-position on the phenyl ring of the ketamine molecule. This modification alters its pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties, influencing its interaction with neurotransmitter systems in the brain.
Pharmacological Mechanisms
Research suggests that deschloroketamine hydrochloride primarily acts as a noncompetitive NMDA receptor antagonist, similar to ketamine. By blocking the activity of N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors, it modulates glutamatergic neurotransmission, leading to dissociative, anesthetic, and hallucinogenic effects. Additionally, DCK exhibits affinity for other receptors, including serotonin and opioid receptors, contributing to its complex pharmacological profile.
Recreational Use and Effects
The recreational use of deschloroketamine hydrochloride has gained traction among individuals seeking novel psychoactive experiences. Users report a range of effects, including dissociation from reality, altered perception of sensory stimuli, time dilation, and introspective insights. Some describe DCK’s effects as similar to those of ketamine, albeit with differences in duration, intensity, and subjective qualities. Its versatility in inducing dissociative states makes it appealing for exploration in various recreational settings.
Therapeutic Potential
While primarily explored for its recreational effects, deschloroketamine hydrochloride has also attracted interest from researchers investigating its potential therapeutic applications. Preliminary studies suggest that it may have utility in the treatment of mood disorders, such as depression and anxiety, as well as chronic pain conditions. Its ability to induce dissociative states and modulate glutamatergic neurotransmission offers promise for addressing underlying neurochemical imbalances and enhancing psychological resilience.
Safety Considerations and Risks
Despite its potential benefits, the use of DCK is not without risks. Like other dissociative substances, it can induce adverse effects such as dissociation, confusion, agitation, hallucinations, and impaired motor function. Prolonged or excessive use may also lead to psychological dependence, tolerance, and withdrawal symptoms upon discontinuation. Furthermore, the purity and potency of DCK obtained from illicit sources may vary, increasing the risk of unintended consequences and harm.
Legal Status and Regulation in USA and Canada
The legal status of DCK varies across different jurisdictions. While it remains unregulated in some countries, others have classified it as a controlled substance due to its psychoactive effects and potential for misuse. Regulatory measures aim to control its availability and minimize associated risks, but enforcement and compliance present ongoing challenges in the context of global drug policy.
Conclusion: Charting New Frontiers
In conclusion, deschloroketamine represents a frontier in the realm of novel psychoactive substances, offering a unique avenue for exploration and discovery. Its distinctive pharmacological properties, combined with its potential therapeutic applications, underscore the need for further research and responsible use. As our understanding of DCK continues to evolve, informed decision-making and harm reduction strategies will remain essential in navigating the complexities of its use. Join us as we chart new frontiers in the fascinating world of deschloroketamine.
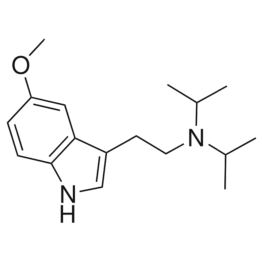
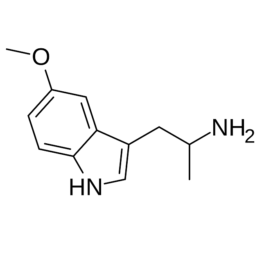
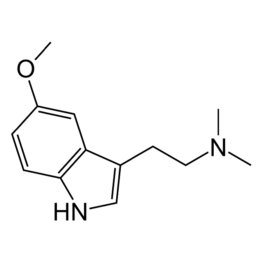
Reviews
There are no reviews yet.